Note
This page was generated from sampling_training_data.ipynb.
Note
If running outside of the Docker image, you might need to set a couple of environment variables manually. You can do it like so:
import os
from subprocess import check_output
os.environ['GDAL_DATA'] = check_output('pip show rasterio | grep Location | awk \'{print $NF"/rasterio/gdal_data/"}\'', shell=True).decode().strip()
os.environ['AWS_NO_SIGN_REQUEST'] = 'YES'
See this Colab notebook for an example.
Sampling training data#
The GeoDataset class#
The GeoDataset is a PyTorch-compatible Dataset implementation that allows sampling images and labels from a Scene.
It comes in two flavors:
Below we explore both in the context of semantic segmentation.
First, let’s define a handy plotting function:
[1]:
def show_windows(img, windows, title=''):
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as patches
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, squeeze=True, figsize=(8, 8))
ax.imshow(img)
ax.axis('off')
# draw windows on top of the image
for w in windows:
p = patches.Polygon(w.to_points(), color='r', linewidth=1, fill=False)
ax.add_patch(p)
ax.autoscale()
ax.set_title(title)
plt.show()
SlidingWindowGeoDataset#
The SlidingWindowGeoDataset allows reading the scene left-to-right, top-to-bottom, using a sliding window.
[2]:
image_uri = 's3://spacenet-dataset/spacenet/SN7_buildings/train/L15-0331E-1257N_1327_3160_13/images/global_monthly_2018_01_mosaic_L15-0331E-1257N_1327_3160_13.tif'
label_uri = 's3://spacenet-dataset/spacenet/SN7_buildings/train/L15-0331E-1257N_1327_3160_13/labels/global_monthly_2018_01_mosaic_L15-0331E-1257N_1327_3160_13_Buildings.geojson'
Here we make use of the convenience API, from_uris() (specifically, from_uris()), but we can also use the normal constructor if we want to manually define the RasterSource and LabelSource.
[3]:
from rastervision.core.data import ClassConfig
from rastervision.pytorch_learner import (
SemanticSegmentationSlidingWindowGeoDataset, SemanticSegmentationVisualizer)
import albumentations as A
class_config = ClassConfig(
names=['background', 'building'],
colors=['lightgray', 'darkred'],
null_class='background')
ds = SemanticSegmentationSlidingWindowGeoDataset.from_uris(
class_config=class_config,
image_uri=image_uri,
label_vector_uri=label_uri,
label_vector_default_class_id=class_config.get_class_id('building'),
image_raster_source_kw=dict(allow_streaming=True),
size=200,
stride=200,
transform=A.Resize(256, 256)
)
2022-12-02 12:39:05:rastervision.core.data.raster_source.rasterio_source: WARNING - Raster block size (2, 1024) is too non-square. This can slow down reading. Consider re-tiling using GDAL.
2022-12-02 12:39:05:rastervision.pipeline.file_system.utils: INFO - Using cached file /opt/data/tmp/cache/s3/spacenet-dataset/spacenet/SN7_buildings/train/L15-0331E-1257N_1327_3160_13/labels/global_monthly_2018_01_mosaic_L15-0331E-1257N_1327_3160_13_Buildings.geojson.
We can read a data sample and the corresponding ground truth from the Dataset like so:
[4]:
x, y = ds[0]
x.shape, y.shape
[4]:
(torch.Size([3, 256, 256]), torch.Size([256, 256]))
And then plot it using the SemanticSegmentationVisualizer:
[5]:
viz = SemanticSegmentationVisualizer(
class_names=class_config.names, class_colors=class_config.colors)
viz.plot_batch(x.unsqueeze(0), y.unsqueeze(0), show=True)

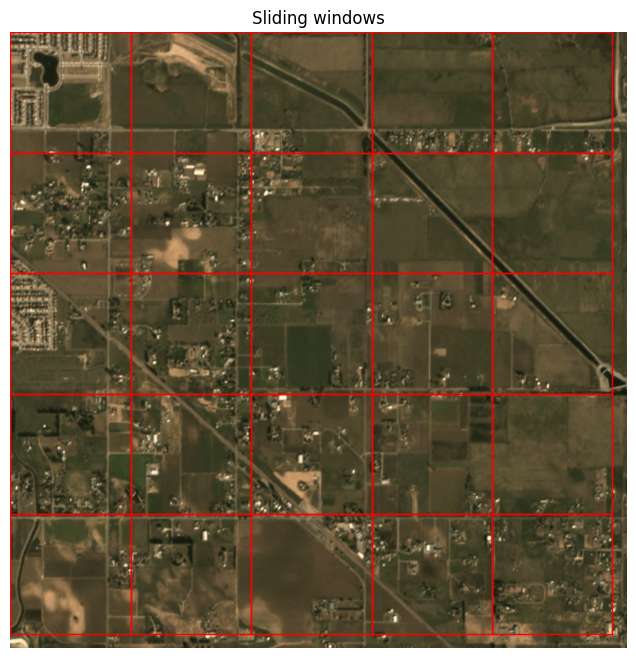
The above was the first sliding window in the dataset. We can visualize what the full set of windows looks like like so:
[6]:
img_full = ds.scene.raster_source[:, :]
show_windows(img_full, ds.windows, title='Sliding windows')
RandomWindowGeoDataset#
The RandomWindowGeoDataset allows reading the scene by sampling random window sizes and locations.
[8]:
image_uri = 's3://spacenet-dataset/spacenet/SN7_buildings/train/L15-0331E-1257N_1327_3160_13/images/global_monthly_2018_01_mosaic_L15-0331E-1257N_1327_3160_13.tif'
label_uri = 's3://spacenet-dataset/spacenet/SN7_buildings/train/L15-0331E-1257N_1327_3160_13/labels/global_monthly_2018_01_mosaic_L15-0331E-1257N_1327_3160_13_Buildings.geojson'
As before, we make use of the convenience API, from_uris() (specifically, from_uris()), but we can also use the normal constructor if we want to manually define the RasterSource and LabelSource.
[9]:
from rastervision.core.data import ClassConfig
from rastervision.pytorch_learner import SemanticSegmentationRandomWindowGeoDataset
import albumentations as A
class_config = ClassConfig(
names=['background', 'building'],
colors=['lightgray', 'darkred'],
null_class='background')
ds = SemanticSegmentationRandomWindowGeoDataset.from_uris(
class_config=class_config,
image_uri=image_uri,
label_vector_uri=label_uri,
label_vector_default_class_id=class_config.get_class_id('building'),
image_raster_source_kw=dict(allow_streaming=True),
# window sizes will randomly vary from 100x100 to 300x300
size_lims=(100, 300),
# resize chips to 256x256 before returning
out_size=256,
# allow windows to overflow the extent by 100 pixels
padding=100
)
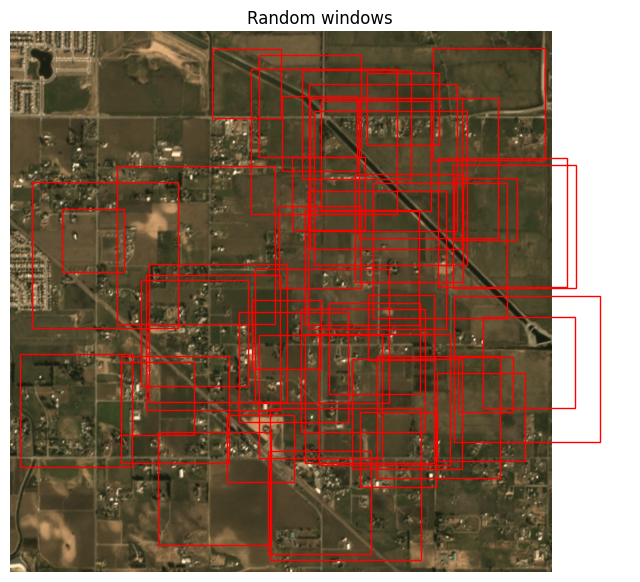
img_full = ds.scene.raster_source[:, :]
windows = [ds.sample_window() for _ in range(50)]
show_windows(img_full, windows, title='Random windows')
2022-09-13 12:52:22:rastervision.pipeline.file_system.utils: INFO - Using cached file /opt/data/tmp/cache/s3/spacenet-dataset/spacenet/SN7_buildings/train/L15-0331E-1257N_1327_3160_13/labels/global_monthly_2018_01_mosaic_L15-0331E-1257N_1327_3160_13_Buildings.geojson.
[10]:
x, y = ds[0]
viz.plot_batch(x.unsqueeze(0), y.unsqueeze(0), show=True)
